The Challenge of Security Visibility in the Past
Back in the day, we followed best practices to configure our services securely. However, there was always the question: Did we actually configure everything correctly? Even if we used tools to identify misconfigurations, they rarely provided a comprehensive view across all services, infrastructure and environments.
With cloud computing, Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) tools have closed this gap. These tools will detect hundreds or even thousands of misconfigurations in your cloud environment. However, having more findings does not necessarily mean a system is more secure. The key is to understand security issues in context - prioritizing and addressing the most critical risks first.
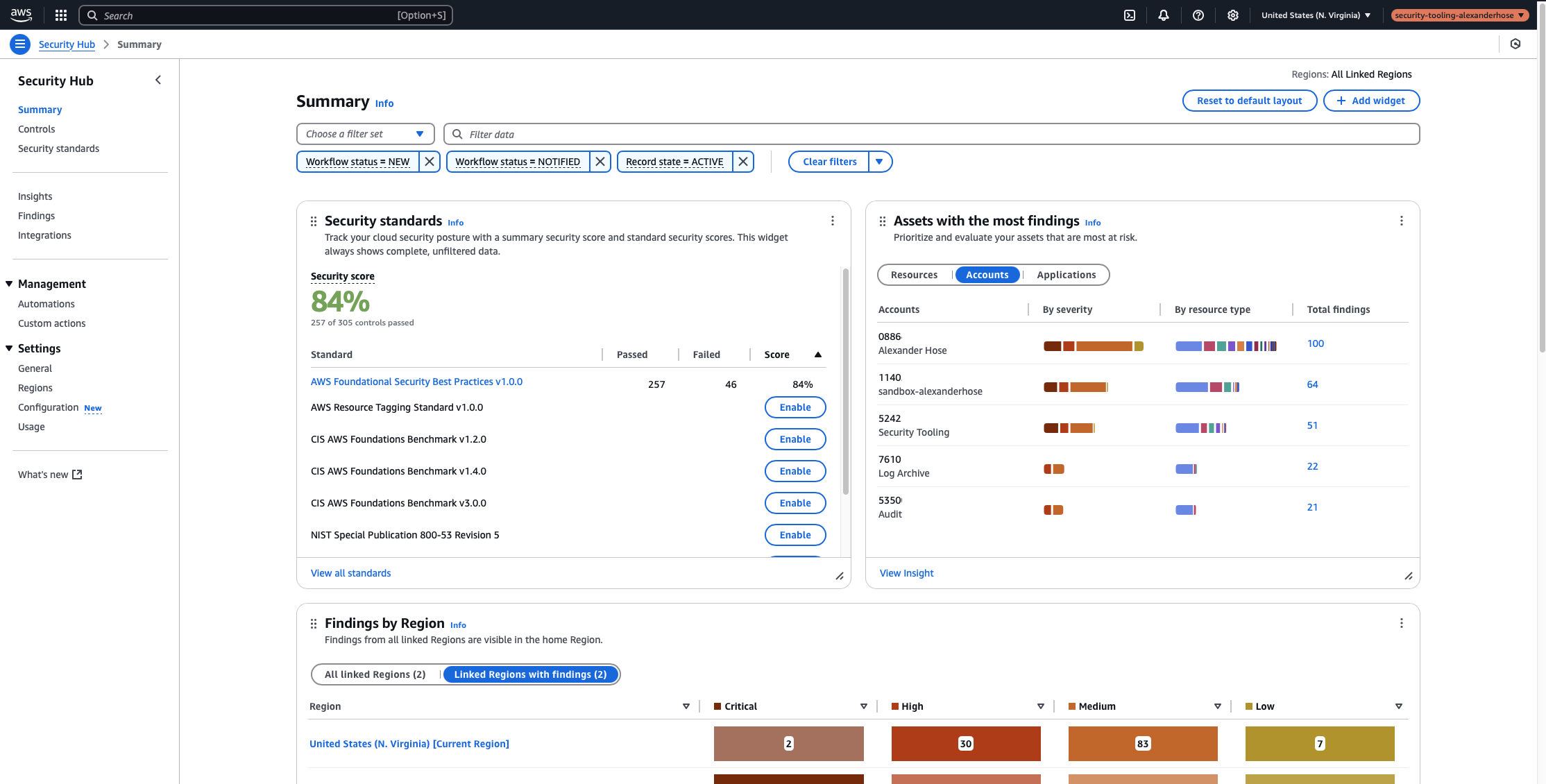
This article is not about analyzing findings in context, but rather about getting a complete view of security findings across an AWS Organization. AWS Security Hub enables this by providing a central dashboard to manage and monitor security findings across all accounts
Step 1: Enabling AWS Config for the Organization
Before we enable AWS Security Hub, we need to configure AWS Config across the entire organization in the management account. AWS Config continuously records configuration changes to AWS resources, which is essential for Security Hub to assess compliance.
To enable AWS Config for the whole AWS Organization, run the following command:
~ $ aws organizations enable-aws-service-access --service-principal=config.amazonaws.com
~ $ aws organizations enable-aws-service-access --service-principal=config-multiaccountsetup.amazonaws.com
~ $ aws organizations list-aws-service-access-for-organization
{
"EnabledServicePrincipals": [
{
"ServicePrincipal": "config.amazonaws.com",
"DateEnabled": "2025-03-17T22:27:27.405000+00:00"
},
{
"ServicePrincipal": "config-multiaccountsetup.amazonaws.com",
"DateEnabled": "2025-03-17T22:38:23.487000+00:00"
}
]
}Next, we need to register a delegated administrator for AWS Config. I recommend using the security tooling account for this purpose:
~ $ aws organizations register-delegated-administrator --service-principal=config.amazonaws.com --account-id <SECURITY_ACCOUNT_ID>
~ $ aws organizations list-delegated-administrators --service-principal=config.amazonaws.com
{
"DelegatedAdministrators": [
{
"Id": "<SECURITY_ACCOUNT_ID>",
"Arn": "arn:aws:organizations::<ORG_ID>:account/o-xxxxxxxxxx/<SECURITY_ACCOUNT_ID>",
"Email": "[email protected]",
"Name": "Security Tooling",
"Status": "ACTIVE"
}
]
}
~ $ aws organizations register-delegated-administrator --service-principal=config-multiaccountsetup.amazonaws.com --account-id <SECURITY_ACCOUNT_ID>
~ $ aws organizations list-delegated-administrators --service-principal=config-multiaccountsetup.amazonaws.com
{
"DelegatedAdministrators": [
{
"Id": "<SECURITY_ACCOUNT_ID>",
"Arn": "arn:aws:organizations::<ORG_ID>:account/o-xxxxxxxxxx/<SECURITY_ACCOUNT_ID>",
"Email": "[email protected]",
"Name": "Security Tooling",
"Status": "ACTIVE"
}
]
}Enabling AWS Config ensures that Security Hub has access to the configuration data needed to evaluate security findings. Without AWS Config, Security Hub would be unable to perform security assessments.
Step 2: Configuring AWS Config and Setting Up an Aggregator
Now that AWS Config is enabled across the organization, we need to properly configure it in the security tooling account and set up an AWS Config aggregator. This will allow us to centralize all configuration data and security findings in one place.
Configuring AWS Config in the Security Tooling Account
To start, we need to configure AWS Config in the Security Tooling Account so it continuously records configuration changes across all AWS resources:
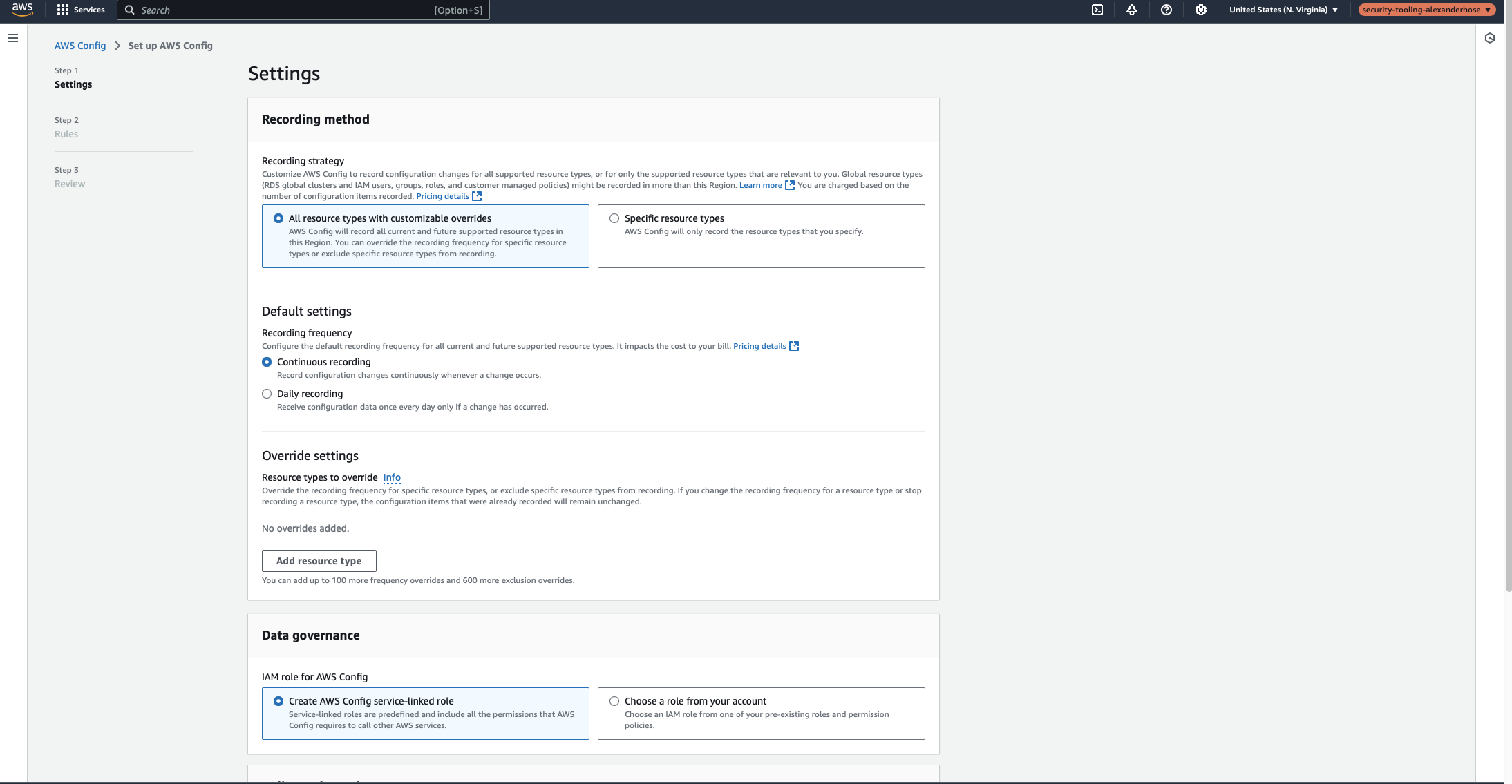
- Resource recording: Select “All resources” to ensure complete visibility.
- Recording frequency: Choose “Continuous recording” to capture changes in real time.
Setting Up the AWS Config Aggregator
Now that AWS Config is active in the Security Tooling Account, we need to aggregate configuration data from all accounts in the organization into this central account.
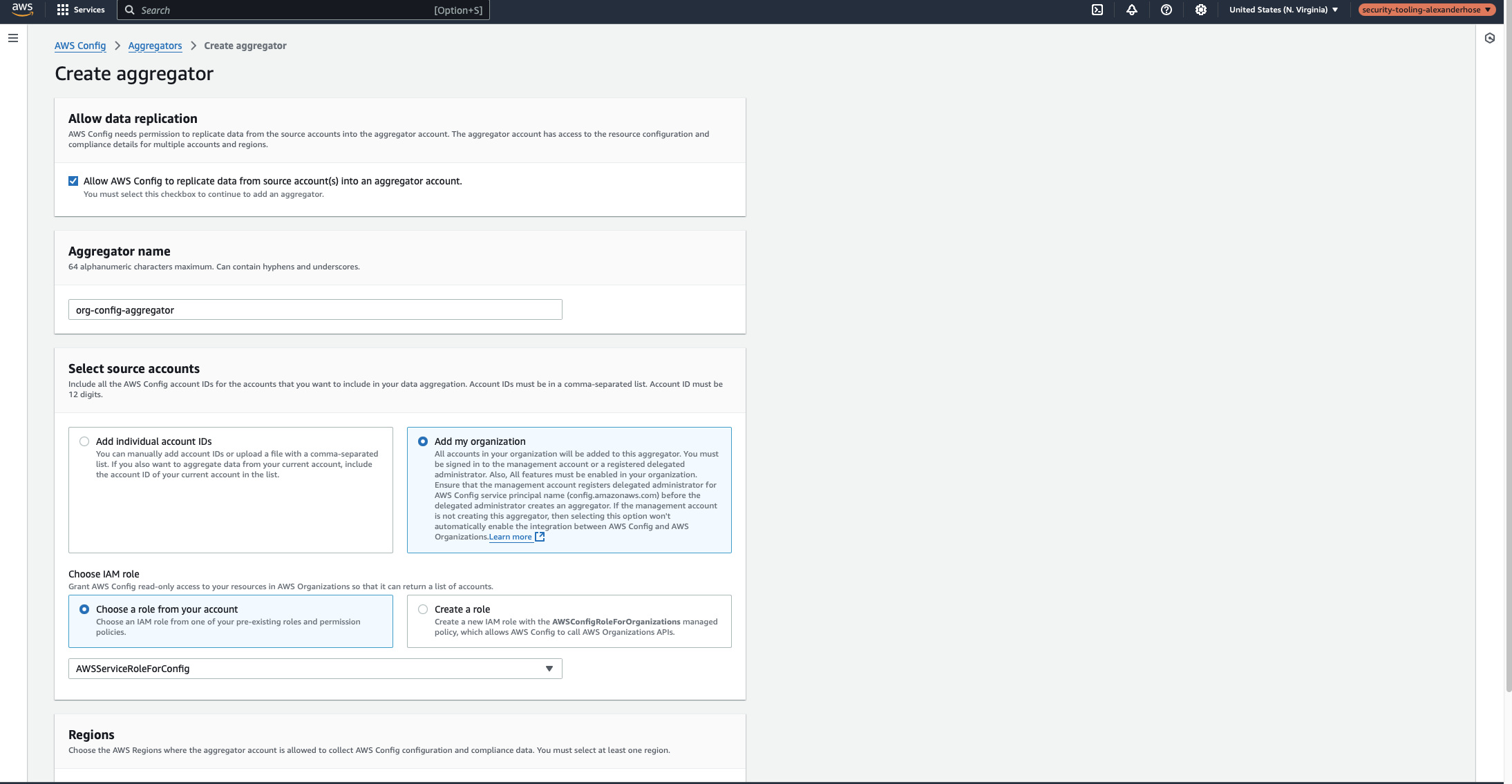
- Regions: Select “All AWS Regions”, or choose specific regions based on your organization's allowed regions.
- IAM Role: Choose
AWSServiceRoleForConfig, which was created when enabling AWS Config for the organization.
After a few minutes, you can check the Aggregators page to verify that all accounts and regions are reporting data correctly. If any accounts are missing, ensure AWS Config is enabled for them.
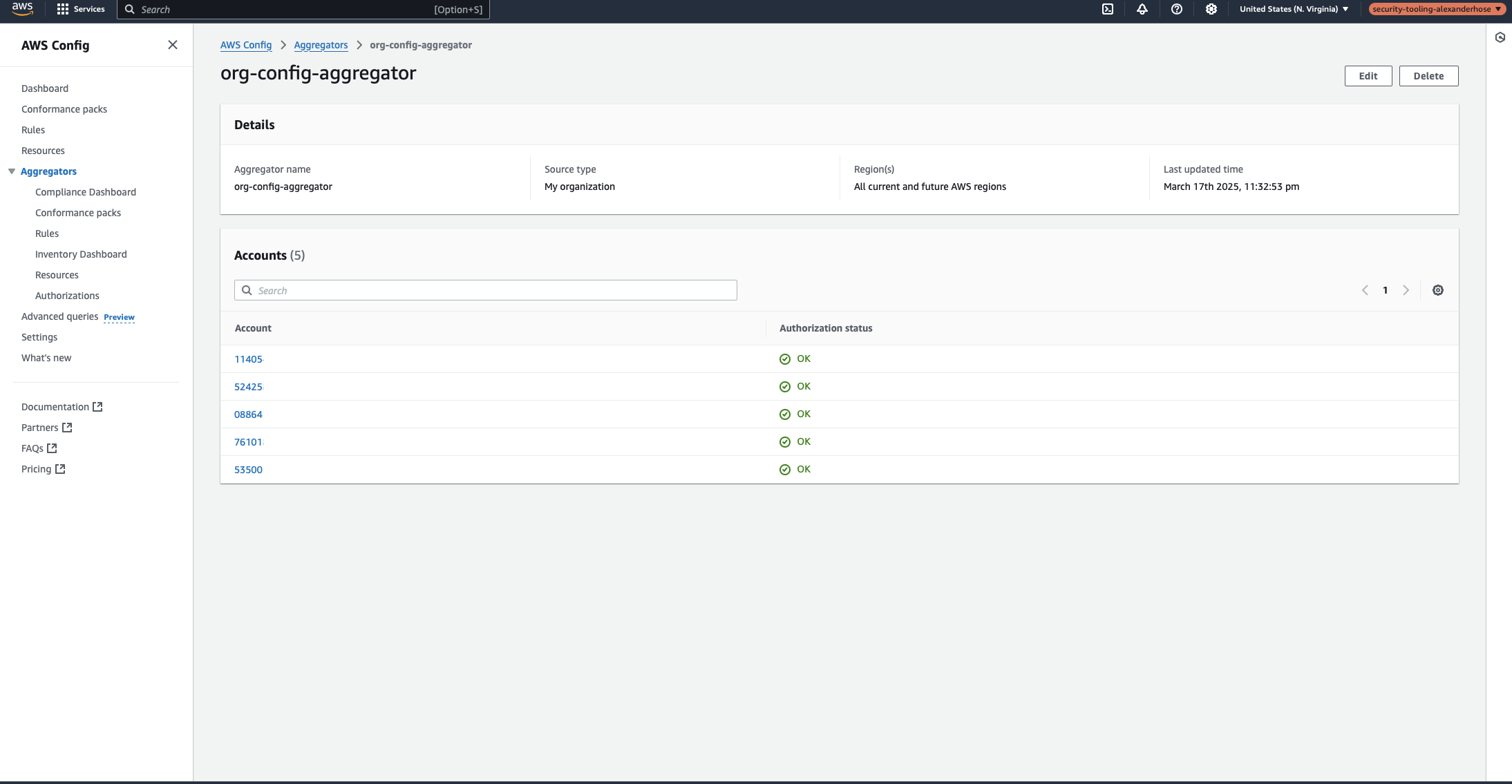
Step 3: Setting Up AWS Security Hub
Now that AWS Config and the aggregator are in place, the next step is to enable AWS Security Hub. Security Hub provides a centralized view of security findings across all AWS accounts in the organization.
Enabling Security Hub for the Entire Organization
To integrate Security Hub across all AWS accounts, trusted access must be enabled so Security Hub can operate at the organizational level.
~ $ aws organizations enable-aws-service-access --service-principal=securityhub.amazonaws.com
~ $ aws securityhub enable-organization-admin-account --admin-account-id <SECURITY_TOOLING_ACCOUNT_ID>
~ $ aws organizations list-delegated-administrators --service-principal=securityhub.amazonaws.com
{
"DelegatedAdministrators": [
{
"Id": "<SECURITY_TOOLING_ACCOUNT_ID>",
"Arn": "arn:aws:organizations::<ORGANIZATION_ID>:account/o-xxxxxxxxxx/<SECURITY_TOOLING_ACCOUNT_ID>",
"Email": "[email protected]",
"Name": "Security Tooling",
"Status": "ACTIVE",
"JoinedMethod": "CREATED",
"JoinedTimestamp": "2025-03-16T22:30:26.507000+00:00",
"DelegationEnabledDate": "2025-03-18T22:24:44.429000+00:00"
}
]
}At this point, Security Hub is active across your organization.
Configuring Security Hub in the Security Tooling Account
The next step is to activate Security Hub in the security tooling account. At this stage, it is recommended not to enable any security standards yet, as these will be in the next step.
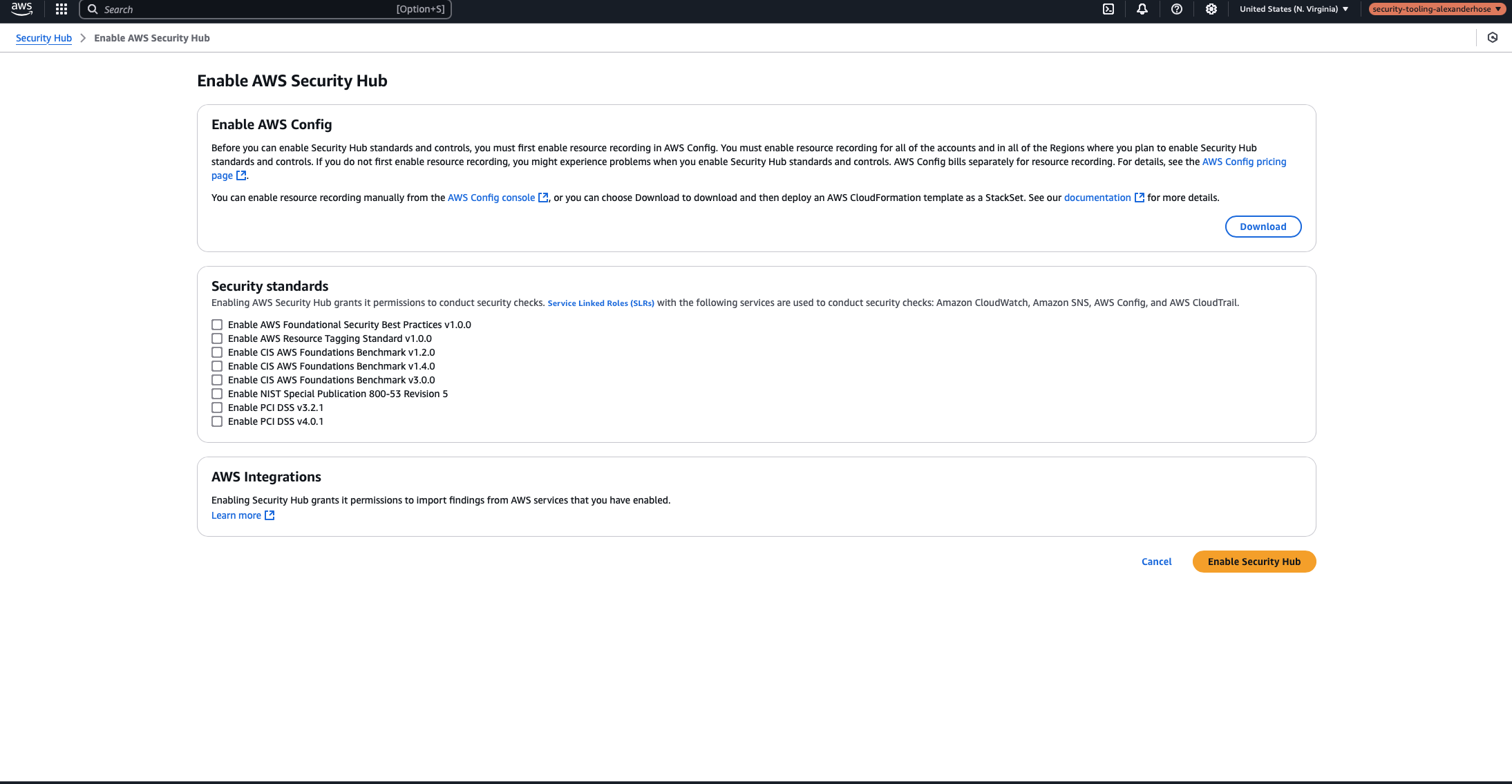
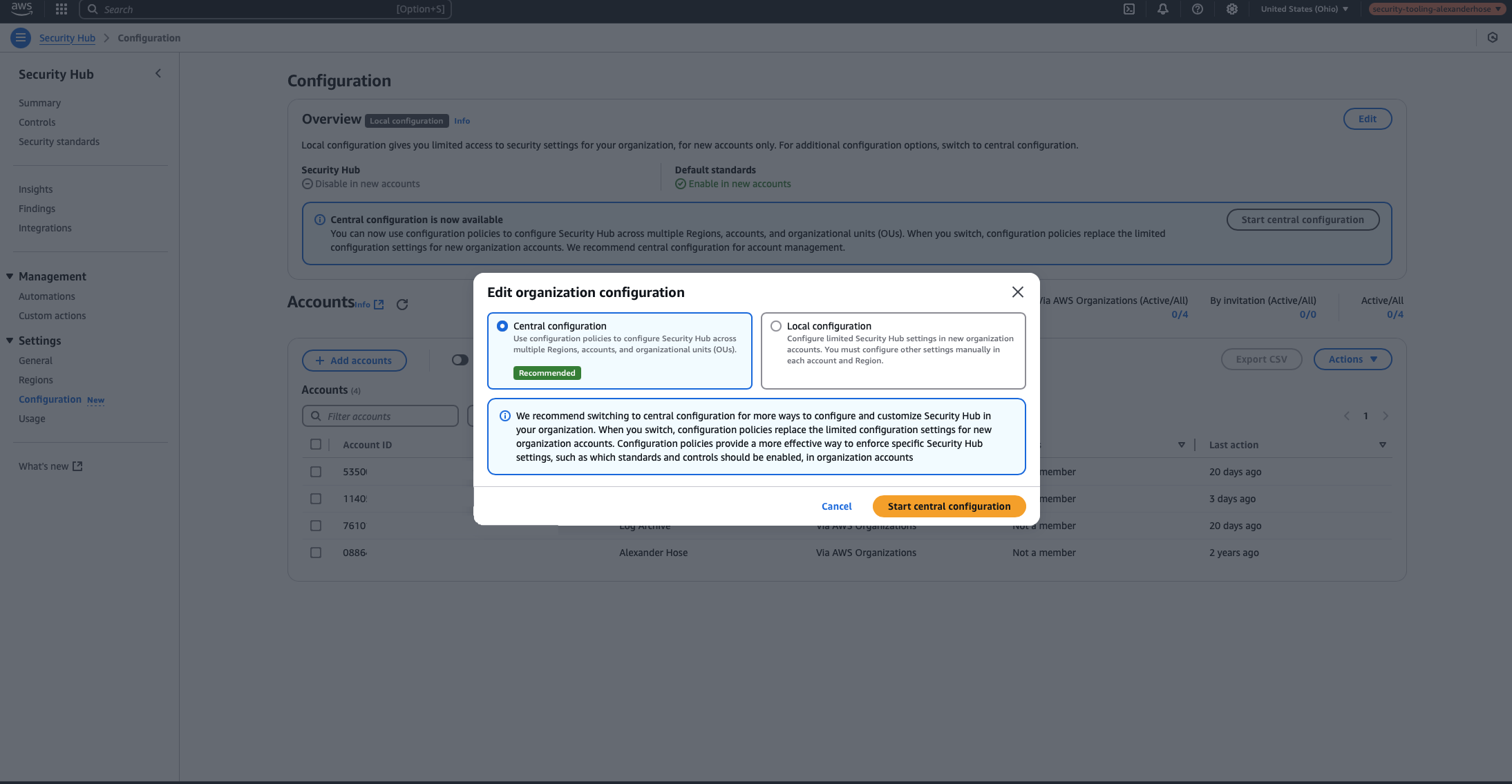
Centralized vs. Local Configuration
Before configuring security standards, it's important to decide whether to use a centralized configuration or allow each account to configure its own settings (local configuration).
With local configuration, each account can independently enable Security Hub and choose which security standards to apply. While this provides flexibility, it also leads to inconsistencies across accounts. Some accounts may enable different standards or none at all, making it difficult to enforce a uniform security posture across the organization.
Instead, I recommend using a centralized configuration to maintain control and consistency. With this approach, the security tooling account acts as the administrator, defining which standards apply to all accounts. This ensures that security findings are assessed uniformly and that no account is left unmonitored. Additionally, centralized management simplifies reporting and reduces operational overhead, as security teams don't have to manually review each account’s configuration.
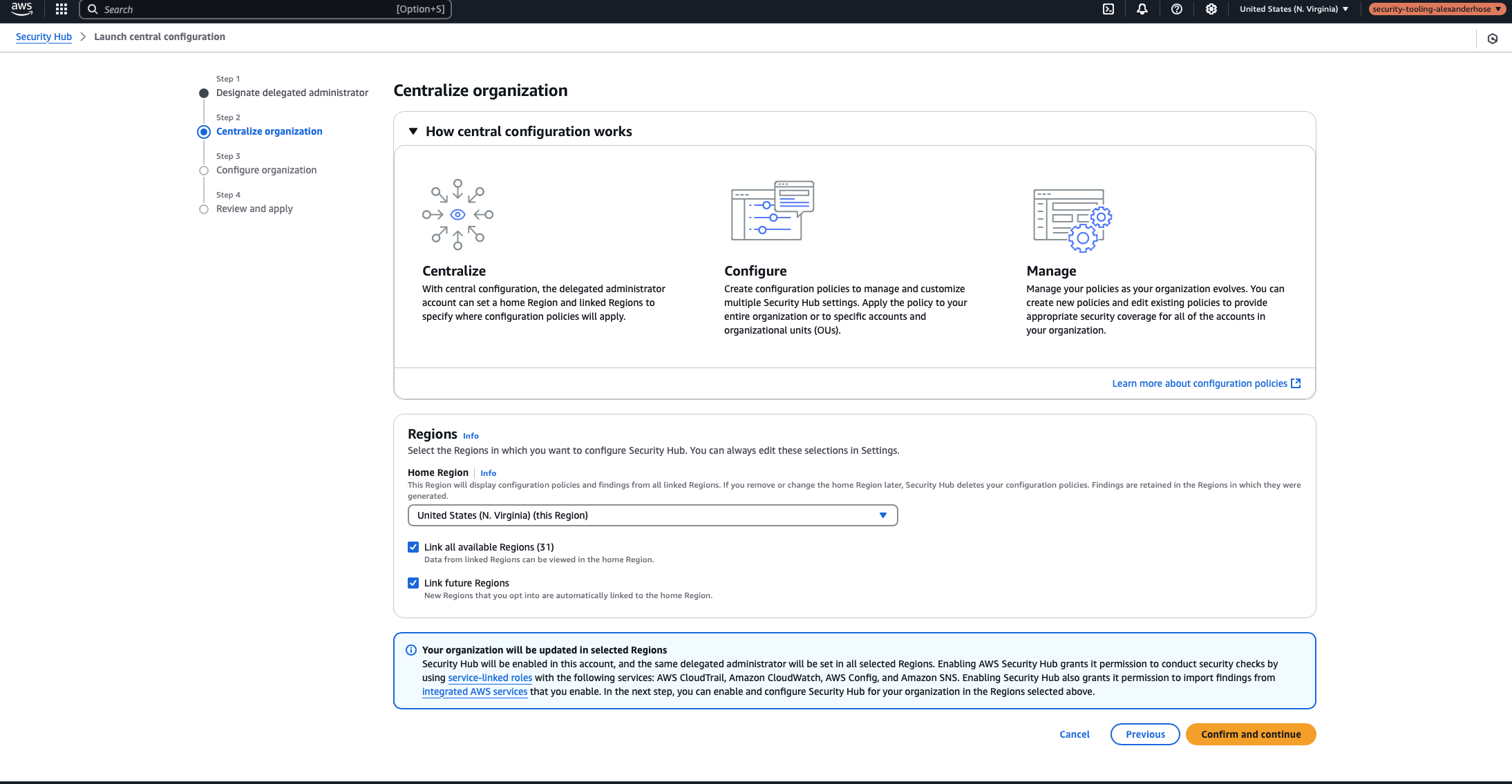
During the configuration the first decision is selecting a Home Region for Security Hub. This is the primary region where Security Hub will store findings and manage organization-wide security settings. I recommend choosing the region where most of your workloads are deployed.
Additionally, you need to decide whether future regions should be linked automatically. This setting depends on your organization’s policies:
- If your organization operates in multiple regions and may expand to others, enabling future regions ensures that Security Hub automatically covers any newly supported regions.
- If your organization restricts workloads to specific regions (e.g., only two approved regions), it’s best to limit Security Hub to those regions to prevent unnecessary costs and complexity.
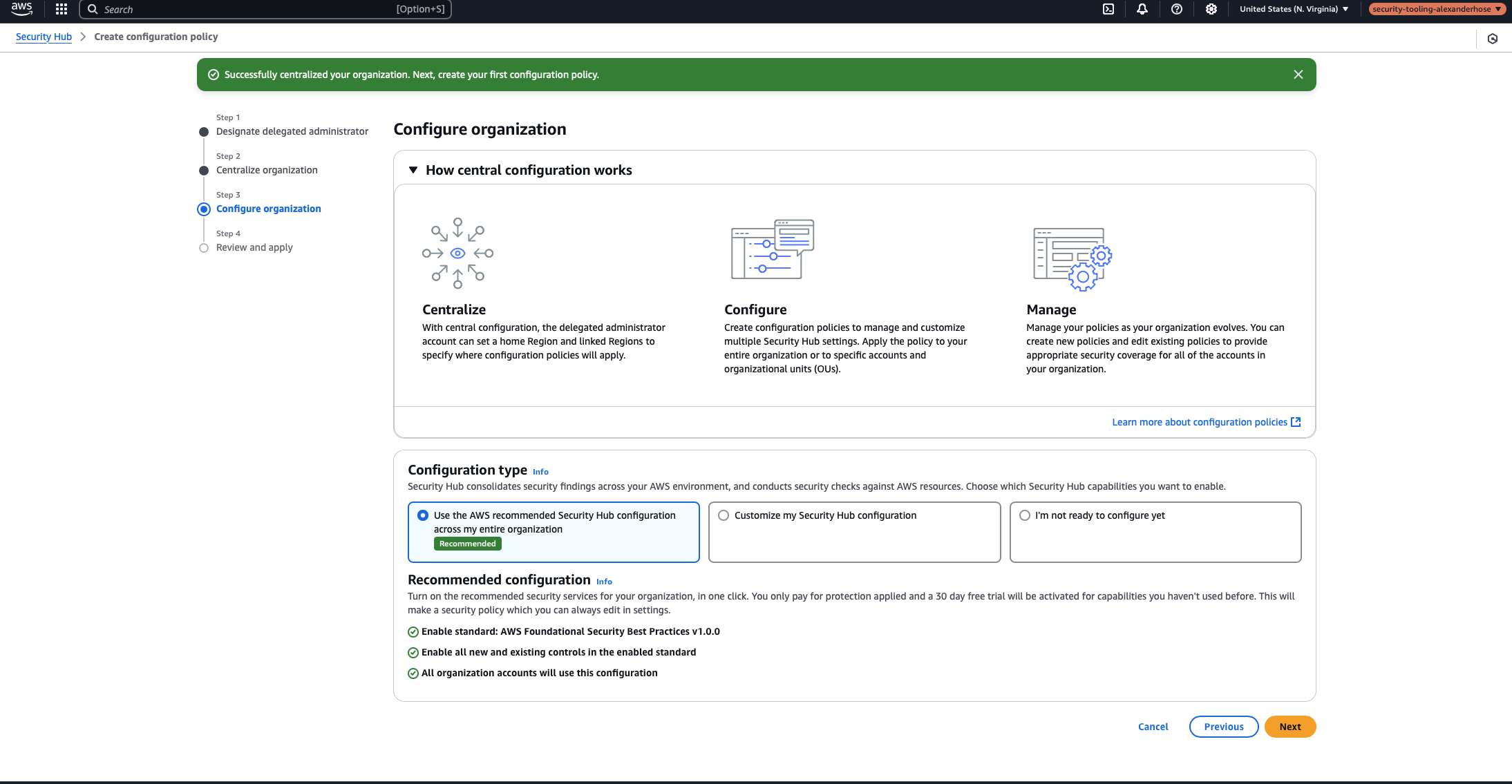
Next, you must choose the configuration type. For most cases, I recommend configuring standards right away, but we can also adjust the configuration later again. When choosing which standards to apply, consider the compliance requirements and security objectives of your organization.
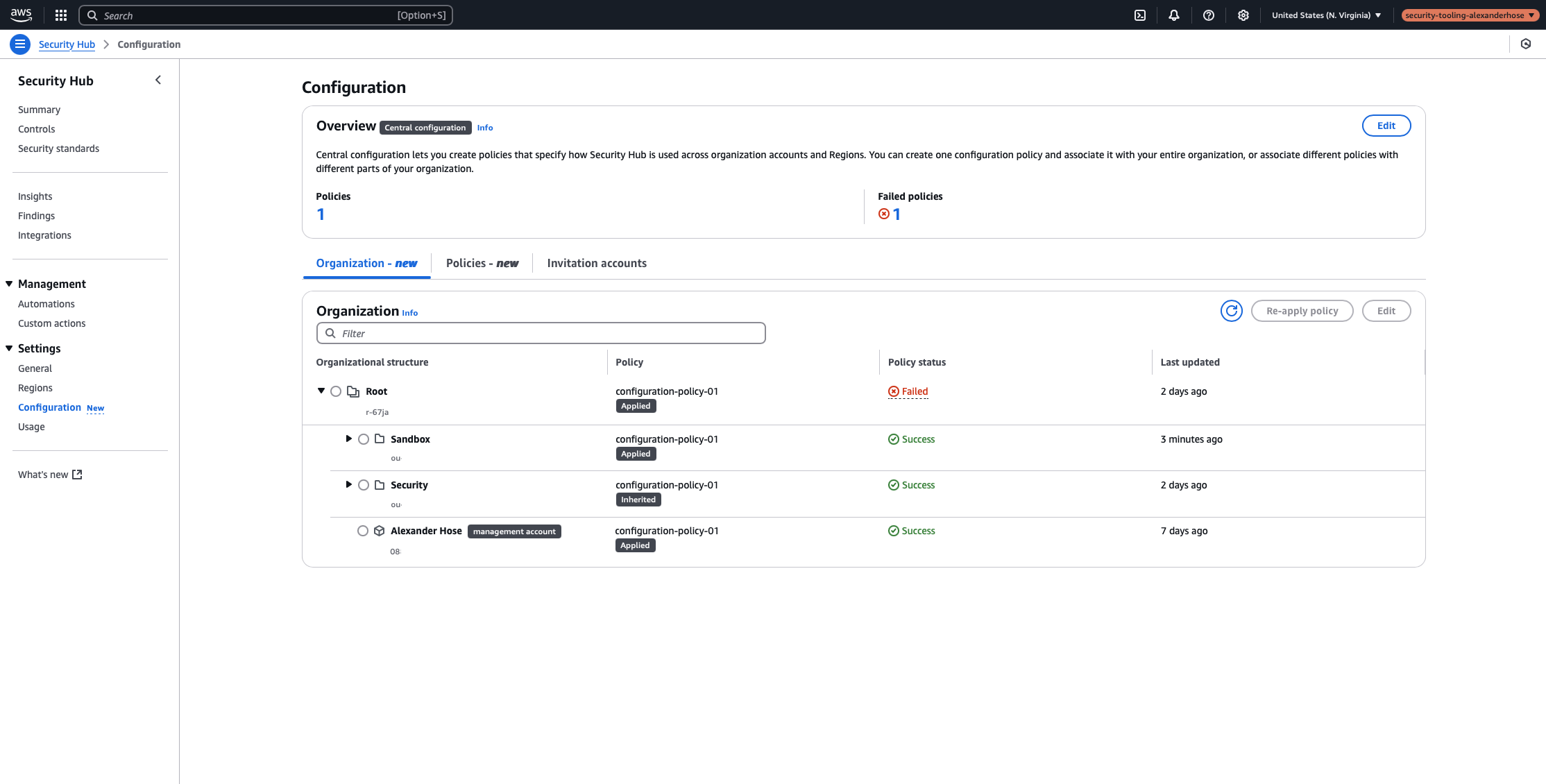
It may take up to 24 hours for all accounts to be fully enrolled in Security Hub. Once onboarding is complete, the Security Hub dashboard will provide an overview of security findings across the organization.
Automatically Enrolling New Accounts
To ensure that new accounts are automatically added to Security Hub, enable auto-enrollment with the following command:
~ $ aws securityhub update-organization-configuration --auto-enableWith this setting enabled, Security Hub will automatically include any newly created or added accounts.
Wrapping Up
With AWS Security Hub fully configured, all accounts in the organization are now centrally monitored. By enabling AWS Config, setting up an aggregator, and enforcing security standards through a centralized configuration, we ensure that all findings and misconfigurations are collected in one place.
Security Hub incurs costs based on the number of security checks, so it’s important to carefully plan which security controls to enable. Enabling too many controls without prioritization may lead to unnecessary expenses.
Additionally, having more findings does not necessarily mean better security. The key is to focus on high-priority misconfigurations and security risks rather than trying to resolve every minor issue. Findings should be analyzed in context, ensuring that remediation efforts target the most critical risks first.
With everything in place, Security Hub is a powerful tool for managing security across the entire AWS Organization.





Member discussion